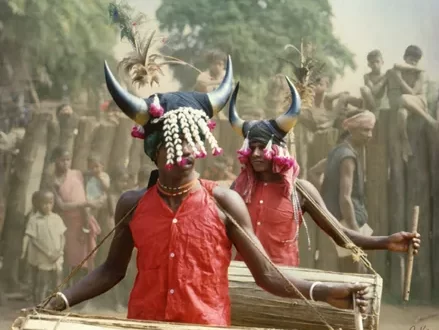The Integral Role of Women in Tribal Families in India
India’s tribal communities, comprising diverse ethnic, linguistic, and cultural groups, have maintained rich traditions and customs for centuries. Central to these traditions is the role of women within the family structure, which is deeply intertwined with cultural, social, economic, and spiritual dimensions. In this comprehensive exploration, we delve into the multifaceted roles that women play in tribal families across India, considering the historical, cultural, and contemporary contexts that shape their experiences and contributions.

Historical and Cultural Context about Tribal Women:
The role of women in tribal families in India is deeply rooted in historical and cultural contexts that vary across different indigenous communities. India’s tribal societies have diverse social structures, belief systems, and customary practices, yet common threads of matriarchal influence, reverence for nature, and community-centric living can be observed.
Historically, many tribal communities in India have been matrilineal or matrilocal, where descent and inheritance are traced through the female line, and women wield significant authority within the family and community. This matriarchal legacy is evident in practices such as matrilineal inheritance of property, participation in decision-making processes, and the transmission of cultural knowledge from mother to daughter.
Experience the charm of Tribal rural living – Tour with us
Furthermore, tribal cultures in India often embody a deep connection with nature and the environment, viewing women as caretakers of the land and guardians of traditional ecological knowledge. Women’s roles in agriculture, foraging, and herbal medicine reflect their intimate relationship with the natural world and their indispensable contributions to the sustenance of their families and communities.

Economic Contributions by Women in Tribal:
In tribal societies across India, women are integral to the economic well-being of their families, engaging in a variety of livelihood activities that sustain household needs and contribute to community resilience. Traditional occupations such as agriculture, animal husbandry, forest gathering, and handicrafts often rely heavily on women’s labor and expertise.
In many tribal communities, women are the primary cultivators of food crops, tending to fields, sowing seeds, and harvesting crops alongside men. Their knowledge of indigenous farming techniques, crop diversity, and soil conservation practices contributes to food security and agricultural sustainability in often marginal and ecologically fragile environments.
Moreover, women in tribal families are skilled artisans, producing a wide range of handicrafts including weaving, pottery, basketry, and beadwork. These crafts not only serve as sources of income but also embody cultural identities, traditions, and artistic expressions that are passed down through generations.
Family and Social Structure:
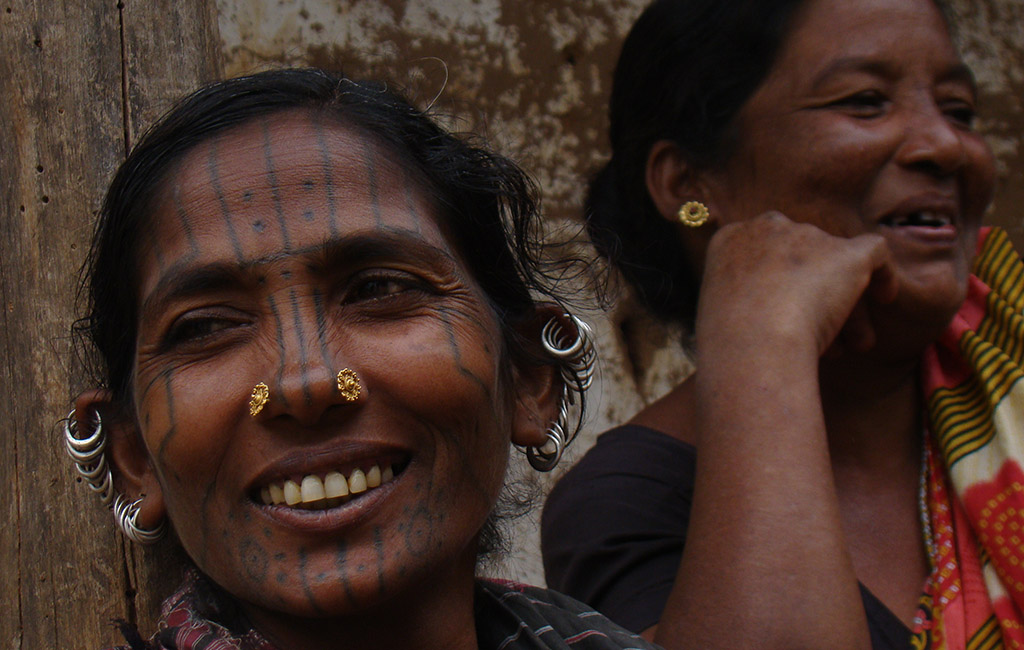
Within tribal families in India, women play central roles in maintaining familial and social cohesion, nurturing relationships, and fostering community solidarity. The extended family structure prevalent in many tribal communities provides a supportive network where women fulfill diverse responsibilities spanning childcare, eldercare, domestic chores, and community leadership.
Women often serve as the primary caregivers for children, imparting cultural values, traditions, and survival skills through storytelling, songs, and rituals. Their nurturing role extends beyond immediate family members to include the broader community, where they offer emotional support, guidance, and practical assistance to neighbors, relatives, and fellow community members.
Moreover, women in tribal societies often serve as mediators and peacemakers, resolving conflicts through dialogue, consensus-building, and traditional dispute resolution mechanisms. Their role in conflict resolution reinforces social harmony, reconciliation, and the maintenance of peaceful coexistence within the community.
Spiritual and Ceremonial Roles:
Spirituality is deeply intertwined with everyday life in tribal communities in India, with women often playing central roles in religious ceremonies, rituals, and healing practices. Many indigenous cultures venerate female deities and goddesses, attributing divine powers to women as creators, nurturers, and protectors of life.
Experience the charm of Tribal rural living – Tour with us
Women in tribal families often serve as custodians of sacred knowledge, rituals, and ceremonies, preserving ancient traditions and transmitting spiritual teachings to future generations. They lead prayers, perform rituals, and conduct ceremonies that mark important life events such as birth, puberty, marriage, and death, infusing these rites with symbolic meanings, cultural significance, and communal celebrations.
Furthermore, women in tribal societies possess specialized knowledge of medicinal plants, healing techniques, and spiritual practices that are integral to holistic well-being and healthcare. As herbalists, midwives, and healers, they provide essential healthcare services, addressing physical, emotional, and spiritual ailments within their communities.
Challenges and Resilience:

Despite the invaluable contributions they make, women in tribal families in India face numerous challenges, including gender-based discrimination, economic marginalization, lack of access to education and healthcare, and the erosion of traditional knowledge systems. Patriarchal norms, caste hierarchies, and developmental interventions often exacerbate these challenges, perpetuating cycles of poverty, inequality, and social exclusion.
However, despite these obstacles, women in tribal communities demonstrate remarkable resilience, resourcefulness, and agency in navigating adversities and advocating for their rights and well-being. Grassroots movements led by indigenous women have emerged across India, demanding recognition, representation, and empowerment within their communities and beyond.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, the role of women in tribal families in India is multifaceted, dynamic, and indispensable, shaping the cultural vitality, social cohesion, and economic resilience of indigenous communities. From agricultural labor and handicraft production to childcare, spiritual leadership, and community activism, women’s contributions permeate every aspect of tribal life, enriching cultural diversity and strengthening social fabric.
Understanding and honoring the roles of women in tribal families requires recognizing their agency, autonomy, and inherent dignity as individuals and community leaders. By addressing systemic barriers, promoting gender equality, and amplifying women’s voices and contributions, we can support the empowerment and well-being of indigenous women in India and ensure the preservation of their rich cultural heritage for generations to come.